今天三旬老汉又双叒叕绝杀了!开心!再水一篇!
在前一篇文章中,提到了redisDb中有两个属性是专门用于阻塞命令的,本文就探究一下阻塞命令的实现。
阻塞命令
redis 针对list类型,实现了BLPOP、BRPOP和BRPOPLPUSH三个特殊的阻塞命令,这些命令是LPOP等命令的阻塞版本,在给定list中没有任何数据供弹出时就会阻塞,直到有值或超时断开。
私认为这个阻塞命令配合普通的LPOP等命令比订阅发布更适合做为消息队列,并且还能通过阻塞命令避免轮训或设定优先级高的消费者。
以BLPOP为例探究一波内部实现。
BLPOP
BLPOP和BRPOP最终会调用同一个通用函数blockingPopGenericCommand:
void blockingPopGenericCommand(client *c, int where) { // RPOP和LPOP的通用实现
robj *o;
mstime_t timeout;
int j;
// 校验阻塞时间参数
if (getTimeoutFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[c->argc-1],&timeout,UNIT_SECONDS)
!= C_OK) return;
// 处理所有监听的key
for (j = 1; j < c->argc-1; j++) {
o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[j]); // 查找是否存在对应list
if (o != NULL) { // 存在对应key
if (o->type != OBJ_LIST) { // 非list
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
return;
} else {
// 普通pop操作
}
}
}
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) { // 如果在事务中直接返回
addReply(c,shared.nullmultibulk);
return;
}
blockForKeys(c, c->argv + 1, c->argc - 2, timeout, NULL); // 如果key不存在或list为空阻塞
}
设置阻塞key
上述代码中大部分同普通pop函数类似,主要对是blockForKeys函数的调用,当client不在事务当中,且所有监听的key都不存在或list为空时,就会调用该函数进行对应key的阻塞:
void blockForKeys(client *c, robj **keys, int numkeys, mstime_t timeout, robj *target) { // 阻塞key 用于阻塞命令
dictEntry *de;
list *l;
int j;
c->bpop.timeout = timeout; // 设置阻塞时间
c->bpop.target = target;
if (target != NULL) incrRefCount(target);
for (j = 0; j < numkeys; j++) {
/* If the key already exists in the dict ignore it. */
if (dictAdd(c->bpop.keys,keys[j],NULL) != DICT_OK) continue; // 将阻塞的key添加到client的bpop.keys字典中
incrRefCount(keys[j]);
/* And in the other "side", to map keys -> clients */
de = dictFind(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j]); // 查找db的blocking_keys中是否存在阻塞的key
if (de == NULL) {
int retval;
/* For every key we take a list of clients blocked for it */
l = listCreate(); // 创建一个adlist对象
retval = dictAdd(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j],l); // 添加到blocking_keys的字典中
incrRefCount(keys[j]);
serverAssertWithInfo(c,keys[j],retval == DICT_OK);
} else {
l = dictGetVal(de);
}
listAddNodeTail(l,c); // 在blocking_keys的对应list中添加上client
}
blockClient(c,BLOCKED_LIST); // 设置客户端阻塞状态
}
void blockClient(client *c, int btype) {
c->flags |= CLIENT_BLOCKED;
c->btype = btype;
server.bpop_blocked_clients++;
}
client结构体为阻塞命令专门准备了两个属性存储阻塞的相关属性:
typedef struct client { // 客户端
// ...
int btype; /* Type of blocking op if CLIENT_BLOCKED. */
blockingState bpop; /* blocking state */
// ...
} client;
typedef struct blockingState {
mstime_t timeout; // 阻塞超时时间
dict *keys; // 阻塞的key字典
robj *target; /* The key that should receive the element,
* for BRPOPLPUSH. */
/* BLOCKED_WAIT */
int numreplicas; /* Number of replicas we are waiting for ACK. */
long long reploffset; /* Replication offset to reach. */
} blockingState;
并且在redisDb中有一个blocking_keys字典属性,每个被阻塞的key都是对应着一个client的list,如果多个client阻塞着同一个key会按照先后顺序添加到list尾部。
并且由于client的flags被设置为CLIENT_BLOCKED,除非存在弹出对象或阻塞超时,server不会主动断开连接。
阻塞超时
同在《redisDb解读》中提到的定期清除过期key一样,redis 也存在对client的定期检测,而bpop.timeout会在client的时间事件循环中被检测,如果当前时间超过阻塞时间,就会返回超时。该监测函数就是clientsCronHandleTimeout:
int clientsCronHandleTimeout(client *c, mstime_t now_ms) { // 校验客户端是否超时
time_t now = now_ms/1000;
if (server.maxidletime &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) && /* no timeout for slaves */
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) && /* no timeout for masters */
!(c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) && /* no timeout for BLPOP */
!(c->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB) && /* no timeout for Pub/Sub clients */
(now - c->lastinteraction > server.maxidletime))
{ // 正常设置的client超时
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Closing idle client");
freeClient(c);
return 1;
} else if (c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) { // 阻塞超时
/* Blocked OPS timeout is handled with milliseconds resolution.
* However note that the actual resolution is limited by
* server.hz. */
if (c->bpop.timeout != 0 && c->bpop.timeout < now_ms) {
/* Handle blocking operation specific timeout. */
replyToBlockedClientTimedOut(c); // 设置超时返回
unblockClient(c); // 解除阻塞
} else if (server.cluster_enabled) { // 集群相关操作
/* Cluster: handle unblock & redirect of clients blocked
* into keys no longer served by this server. */
if (clusterRedirectBlockedClientIfNeeded(c))
unblockClient(c);
}
}
return 0;
}
刨除一些列的校验,最核心的是unblockClient这个函数:
void unblockClient(client *c) { // 解除阻塞
if (c->btype == BLOCKED_LIST) {
unblockClientWaitingData(c);
} else if (c->btype == BLOCKED_WAIT) {
unblockClientWaitingReplicas(c);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown btype in unblockClient().");
}
/* Clear the flags, and put the client in the unblocked list so that
* we'll process new commands in its query buffer ASAP. */
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_BLOCKED;
c->btype = BLOCKED_NONE;
server.bpop_blocked_clients--;
/* The client may already be into the unblocked list because of a previous
* blocking operation, don't add back it into the list multiple times. */
if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_UNBLOCKED)) { // 将client添加到server的非阻塞list中
c->flags |= CLIENT_UNBLOCKED;
listAddNodeTail(server.unblocked_clients,c);
}
}
void unblockClientWaitingData(client *c) { // 解除client的阻塞
dictEntry *de;
dictIterator *di;
list *l;
serverAssertWithInfo(c,NULL,dictSize(c->bpop.keys) != 0);
di = dictGetIterator(c->bpop.keys); // 获取阻塞的keys
/* The client may wait for multiple keys, so unblock it for every key. */
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) { // 遍历client阻塞的所有key
robj *key = dictGetKey(de);
/* Remove this client from the list of clients waiting for this key. */
l = dictFetchValue(c->db->blocking_keys,key);
serverAssertWithInfo(c,key,l != NULL);
listDelNode(l,listSearchKey(l,c)); // 删除blocking_keys list中的client
/* If the list is empty we need to remove it to avoid wasting memory */
if (listLength(l) == 0) // 删除空list
dictDelete(c->db->blocking_keys,key);
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
/* Cleanup the client structure */
dictEmpty(c->bpop.keys,NULL); // 释放client的bpop.keys占用内存
if (c->bpop.target) {
decrRefCount(c->bpop.target);
c->bpop.target = NULL;
}
}
unblockClientWaitingData函数清空了client->bpoop.keys,并将db中的blocking_keys对应的client删除。
清空完阻塞的各种属性值后,会将client添加到server.unblocked_clients的list中,这个list会在每次时间事件执行之前被检测是否有值,如果存在就返回超时并删除list中对应的client:
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { // 每一次事件循环都会执行该函数
// ...
if (listLength(server.unblocked_clients))
processUnblockedClients();
// ...
}
void processUnblockedClients(void) { // 向非阻塞状态的client返回值
listNode *ln;
client *c;
while (listLength(server.unblocked_clients)) {
ln = listFirst(server.unblocked_clients);
serverAssert(ln != NULL);
c = ln->value;
listDelNode(server.unblocked_clients,ln); // 删除list节点
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_UNBLOCKED;
if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED)) {
if (c->querybuf && sdslen(c->querybuf) > 0) {
processInputBuffer(c); // 向client返回结果
}
}
}
}
因为超时的返回很可能需要跨越事件循环,因此当阻塞命令的阻塞时间并不是精确的,通常都会多一到两个时间事件周期间隔。redis 的默认周期间隔为100ms,正常情况下会多阻塞100-200ms。
正常弹出
当有另一个client对阻塞的key进行push操作时,阻塞的client就会被正常弹出并获取返回值。该监测操作在dbAdd函数中:
void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) { // db添加键值对
sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr); // 复制key
int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val); // 往字典中添加键值对
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == DICT_OK);
if (val->type == OBJ_LIST) signalListAsReady(db, key); // 如果是list对象 判断是否有阻塞命令在监听
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key); // 集群相关操作
}
如果添加的key是list对象,并且处于阻塞中,signalListAsReady就会标识该key已经就绪。
typedef struct readyList { // server的待弹出list节点
redisDb *db;
robj *key;
} readyList;
void signalListAsReady(redisDb *db, robj *key) { // 标识某个阻塞key已经就绪
readyList *rl;
/* No clients blocking for this key? No need to queue it. */
if (dictFind(db->blocking_keys,key) == NULL) return;
/* Key was already signaled? No need to queue it again. */
if (dictFind(db->ready_keys,key) != NULL) return;
/* Ok, we need to queue this key into server.ready_keys. */
rl = zmalloc(sizeof(*rl));
rl->key = key;
rl->db = db;
incrRefCount(key);
listAddNodeTail(server.ready_keys,rl); // 将ready_list添加到serverr.ready_keys的尾部
/* We also add the key in the db->ready_keys dictionary in order
* to avoid adding it multiple times into a list with a simple O(1)
* check. */
incrRefCount(key);
serverAssert(dictAdd(db->ready_keys,key,NULL) == DICT_OK); // 将key添加到db的ready_keys字典中
}
server的ready_keys是一个list,每个节点都是一个readyList对象,保存了key和对应的db。而在最终的阻塞返回是在handleClientsBlockedOnLists函数中,该函数会在每次命令执行完成后被检测调用,以确保不会被其他pop命令先弹出:
int processCommand(client *c) { // 执行命令
// ...
/* Exec the command */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{ // 事务
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else { // 普通命令
call(c,CMD_CALL_FULL); // 调用命令对应函数
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnLists(); // 处理阻塞key
}
return C_OK;
}
通过在每次命令完成后对ready_keys进行检测,从而保证阻塞的key不会被其他的pop命令弹出。
void handleClientsBlockedOnLists(void) { // 处理list阻塞弹出返回
while(listLength(server.ready_keys) != 0) {
list *l;
l = server.ready_keys;
server.ready_keys = listCreate(); // 将ready_keys置空
while(listLength(l) != 0) { // 遍历server.ready_keys
listNode *ln = listFirst(l);
readyList *rl = ln->value;
dictDelete(rl->db->ready_keys,rl->key); // 清除db->ready_keys
robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(rl->db,rl->key); // 查找对应的key
if (o != NULL && o->type == OBJ_LIST) {
dictEntry *de;
de = dictFind(rl->db->blocking_keys,rl->key); // 查找db的blocking_keys 获取阻塞client list
if (de) {
list *clients = dictGetVal(de);
int numclients = listLength(clients);
while(numclients--) { // 遍历clients 如果有足够多的值就都弹出返回
listNode *clientnode = listFirst(clients);
client *receiver = clientnode->value; // 获取client对象
robj *dstkey = receiver->bpop.target;
int where = (receiver->lastcmd &&
receiver->lastcmd->proc == blpopCommand) ?
LIST_HEAD : LIST_TAIL;
robj *value = listTypePop(o,where); // pop对应list
if (value) {
if (dstkey) incrRefCount(dstkey);
unblockClient(receiver); // 解除client的阻塞
if (serveClientBlockedOnList(receiver,
rl->key,dstkey,rl->db,value,
where) == C_ERR)
{ // 如果通知客户端出错就进行回滚,将数据push回list
listTypePush(o,value,where);
}
if (dstkey) decrRefCount(dstkey);
decrRefCount(value);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
if (listTypeLength(o) == 0) {
dbDelete(rl->db,rl->key);
}
}
// 释放临时变量
decrRefCount(rl->key);
zfree(rl);
listDelNode(l,ln);
}
listRelease(l); /* We have the new list on place at this point. */
}
}
小结一波
一个阻塞命令涉及到的数据结构图如下:
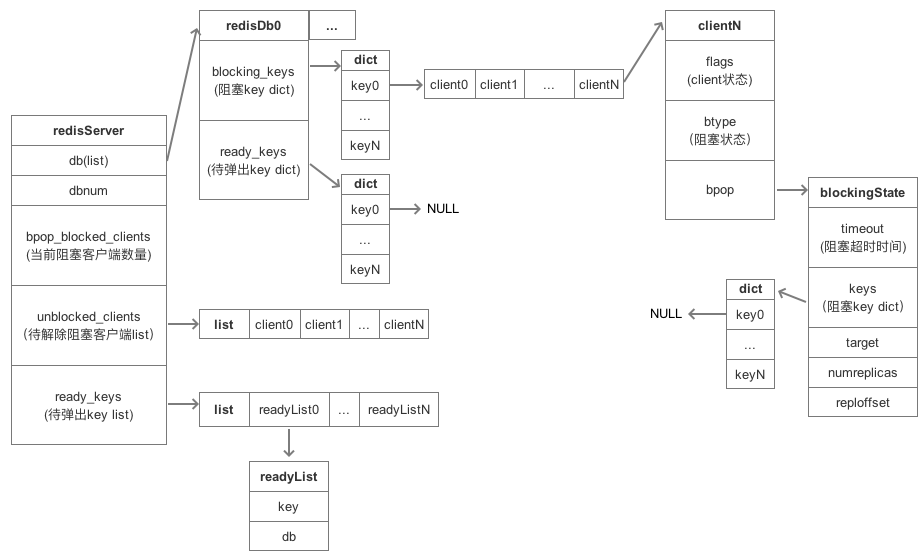
- redisServer都是遍历需求,因此采用list作为存储结构。其中ready_keys需要key加db才能确定一个唯一阻塞值,因此list元素为一个简单的结构体。
- redisDb的blocking_keys用于存储单个db的阻塞key,有精确查找需求,采用dict作为基础数据结构。由于db的阻塞key和client为1对多关系,blocking_keys的value为clients的list。
- redisDb的ready_keys只是起到一个单纯的去重逻辑,db是key阻塞的单位,因此去重逻辑放在db结构体中最为合适。采用dict存储,将value置为NULL,只用到dict的索引的。
- client中的flags和btype用于记录阻塞的一些状态标志,bpop为一个复杂结构体,保存着阻塞超时时间和阻塞keys等,其中keys为dict数据结构,value为NULL,同db的ready_keys。